Flyweight
Flyweight Pattern
플라이웨이트 패턴
객체들 사이에 유사한 데이터를 서로 공유하여 메모리 사용량을 최소화 하는 패턴.
UML
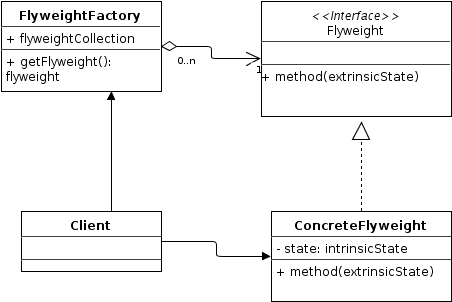 1
1
Flyweight
팩토리를 통해 생성될 즉 플라이웨이트 패턴이 적용될 객체의 인터페이스
ConcreteFlyweight
Flyweight의 구상체
FlyweightFactory
Flyweight를 효율적으로 생성할 팩토리
Client
사용자
예제
자동차에 필요한 요소는 많지만 다음만 고려한다. (Flyweight)
public interface Car {
public void gogo();
public void stop();
public String getColor();
}
Car의 구상체, 본 예제에서 color는 문자열에 불과하지만 비용이 큰 객체라 가정한다.(ConcreteFlyweight)
color의 종류는 자동차 종류나 총 출고량에 비하면 매우 적을 것이다.
public class HyundaiCar implements Car{
private String _color;
public HyundaiCar(String color) {
_color = color;
}
@Override
public void gogo() {
//Car start
}
@Override
public void stop() {
//Car stop
}
@Override
public String getColor() {
return _color;
}
}
객체 생성을 위한 팩토리, 비용이 비싼 color객체를 공유하게 하기 위해 HashMap을 이용해 구현. (FlyweightFactory)
public class HyundaiCarFactory {
private static Map<String, Car> carBluePrint = new HashMap<>();
public static Car createCar(String color)
{
Car newCar = carBluePrint.computeIfAbsent(color, newColor -> {
System.out.println("Create new instance : " + newColor);
return new HyundaiCar(newColor);
});
return newCar;
}
}
클라이언트
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car[] car = new HyundaiCar[5];
car[0] = HyundaiCarFactory.createCar("BLACK");
car[1] = HyundaiCarFactory.createCar("BLACK");
car[2] = HyundaiCarFactory.createCar("WHITE");
car[3] = HyundaiCarFactory.createCar("WHITE");
car[4] = HyundaiCarFactory.createCar("BLACK");
System.out.println("-----");
for (int i=0;i<5;i++) {
String carStr = String.format("car%d : %s", i, car[i].getColor());
System.out.println(carStr);
}
}
}
결과로 출력된 화면이다. 여러 car들을 생성하며 Color는 두번만 새로 생성되었지만, 모든 car들은 color를 가지고 있다.
Create new instance : BLACK
Create new instance : WHITE
-----
car0 : BLACK
car1 : BLACK
car2 : WHITE
car3 : WHITE
car4 : BLACK
참고문헌